定义
在一个方法中定义一个方法骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中,子类可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义其中一个或多个步骤
真实世界类比
怎么泡一壶茶?怎么泡一杯咖啡?
- 把水煮沸
- 用沸水浸泡茶叶/用沸水冲泡咖啡粉
- 把茶倒进辈子/把咖啡倒进杯子
- 加柠檬/加糖和奶
过程泛化后:
- 把水煮沸
- 冲泡
- 把饮品倒进杯子
- 加调料
模板方法就是一组步骤组成的方法,其中每个步骤都可以是抽象的。
场景
泡多种咖啡因饮料
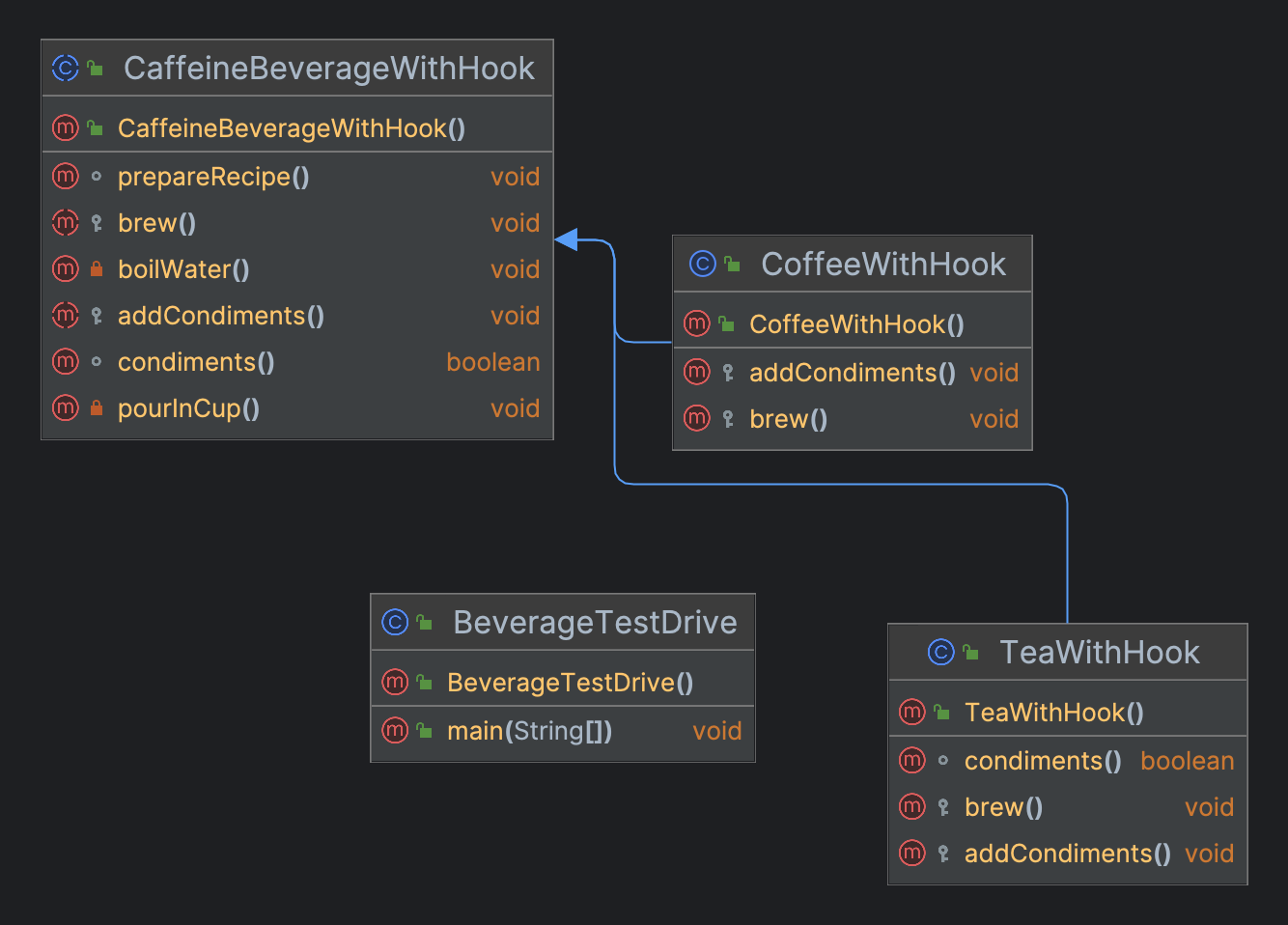
类图
实现
CaffeineBeverageWithHook(咖啡因饮料with钩子)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public abstract class CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
void prepareRecipe() {
boilWater();
brew();
pourInCup();
if (condiments()) {
addCondiments();
}
}
protected abstract void addCondiments();
boolean condiments() {
return true;
}
private void pourInCup() {
System.out.println("Pouring into cup.....");
}
protected abstract void brew();
private void boilWater() {
System.out.println("Boiling water.....");
}
}
CoffeeWithHook …(coffee)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class CoffeeWithHook extends CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
@Override
protected void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding sugar and milk....");
}
@Override
protected void brew() {
System.out.println("Dripping coffee through filter.....");
}
}
TeaWithHook(Tea)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class TeaWithHook extends CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
@Override
protected void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding lemon....");
}
@Override
protected void brew() {
System.out.println("Add tea.....");
}
@Override
boolean condiments() {
return false;
}
}
hook钩子让子类对模版中某些步骤做出反应
BeverageTestDrive
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class BeverageTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TeaWithHook teaWithHook = new TeaWithHook();
teaWithHook.prepareRecipe();
CoffeeWithHook coffeeWithHook = new CoffeeWithHook();
coffeeWithHook.prepareRecipe();
}
}
适用场景
- 当你只希望客户端扩展某个特定算法步骤,而不是整个算法或其结构时,可使用模板方法模式
- 当多个类的算法除一些细微不同之外几乎完全一样时,你可使用该模式
特点
- 优点
- 你可仅允许客户端重写一个大型算法中的特定部分,使得算法其他部分修改对其所造成的影响减小
- 你可将重复代码提取到一个超类中
- 缺点
- 部分客户端可能会受到算法框架的限制
- 通过子类抑制默认步骤实现可能会导致违反里氏替换原则
- 模板方法中的步骤越多,其维护工作就可能会越困难
参考:《Head First 设计模式》